5G is often pitched as the key to faster operations, smarter infrastructure, and real-time visibility. For enterprise leaders, it sounds like the next logical step in digital transformation.
But once the deployment begins, the reality feels very different.
Legacy networks start to buckle. Devices that should have worked together stop talking. Coverage gaps emerge where performance matters most, inside factories, warehouses, and densely packed campuses. Security frameworks that worked for Wi-Fi or 4G suddenly seem incomplete.
The biggest issue? Integration is far more complex than vendors admit. You are not just rolling out new radios. You are rebuilding how your infrastructure moves data, prioritizes traffic, and scales across locations.
This article outlines the seven most common challenges enterprises face during 5G deployment. Each challenge is drawn from real-world experience, not theory. And more importantly, we explore how to solve them with strategies that reduce rework and unlock real performance.
If your 5G deployment is on the roadmap, this is the reality check you need.
Common Challenges in 5G Deployment and Their Solutions
Rolling out 5G inside an enterprise is rarely straightforward. It is not just a matter of upgrading bandwidth or adding more devices. Most challenges come from trying to align new technology with existing infrastructure, processes, and business expectations.
But here’s the thing: solving these challenges is not just about identifying what’s broken. It’s about knowing exactly how to fix it.
In the sections that follow, we explore the seven most common roadblocks enterprises face during 5G deployment. And for each one, we share a field-tested solution drawn from years of real integration work inside enterprise networks.
If your deployment is running into friction or you want to get ahead of the failure points, this breakdown will help you move forward with clarity and confidence.
Let’s look at each challenge and solution, one by one.
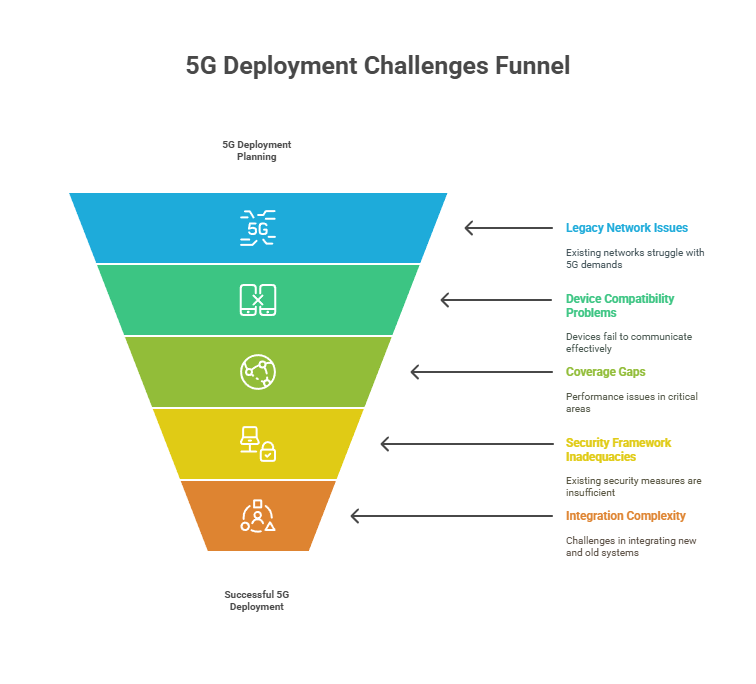
#1. Legacy Infrastructure Bottlenecks
Most enterprises do not start from scratch. They are working with a mix of aging switches, outdated firewalls, overworked VLANs, and Wi-Fi architectures that were never designed for real-time data movement at scale. On the surface, it may look stable. But bring in 5G, and the cracks start to show.
Devices fail to handshake. Throughput drops at the access layer. Latency creeps in where there should be none. This is not a hardware problem. It is a network design problem.
5G can only move as fast as your internal fabric allows. And when that fabric is stitched together from outdated gear or rigid configurations, performance suffers. Worse, the business assumes 5G is underdelivering when the real bottleneck is buried inside the LAN.
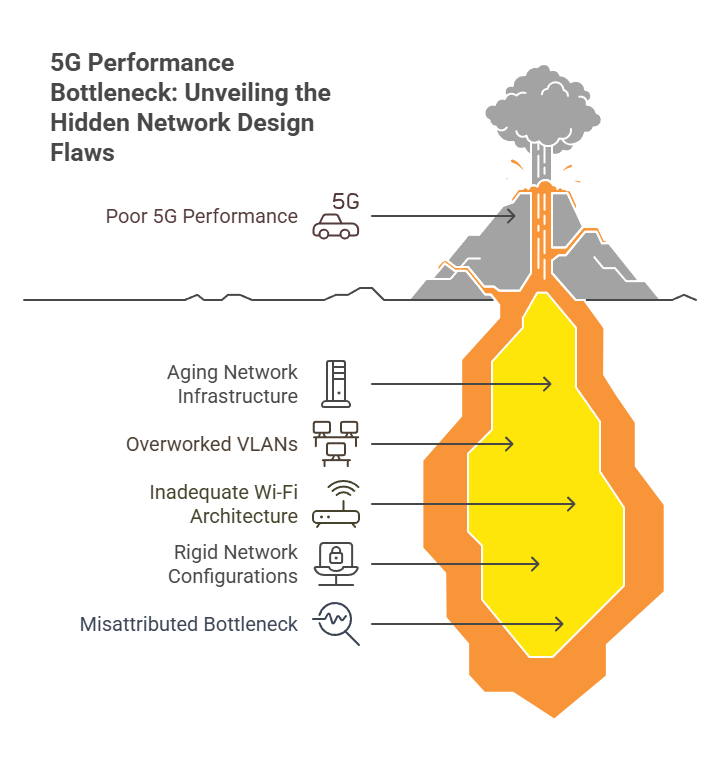
The fix starts with a network readiness audit.
Before a single 5G radio is deployed, your switching, routing, and segmentation need to be reviewed. Moreover, access and distribution layers must be evaluated for throughput, redundancy, and alignment with 5G transport models. Quality of service policies must also be redefined to prioritize time-sensitive workloads. And legacy hardware must be refreshed where it blocks performance.
Enterprises that solve this early deploy faster, scale cleaner, and avoid the blame cycle that always follows a poor rollout.
#2. Spectrum Confusion and Licensing Complexity
Ask any enterprise team deploying 5G for the first time, and you will hear the same hesitation. Where exactly is our spectrum coming from? Can we buy it, lease it, or use something unlicensed? And what happens if we pick the wrong model?
This confusion is not trivial. The spectrum model you choose defines how stable, secure, and scalable your 5G network will be. Get it wrong, and you are stuck with interference, compliance issues, or ongoing costs that kill the business case.
Most enterprises are not equipped to navigate this. They do not have RF specialists on staff. And telecom providers often push spectrum packages that serve their interests, not yours.
The right approach begins with an enterprise-first spectrum strategy.
That means choosing between three paths: leasing licensed spectrum from a telecom operator, using shared spectrum (such as CBRS in the US), or deploying over unlicensed bands like 5 GHz or 6 GHz. Each comes with tradeoffs in interference, control, and cost.
The best integrators start by mapping your operational environment: is it indoors or outdoors, urban or rural, low-density or high-traffic?
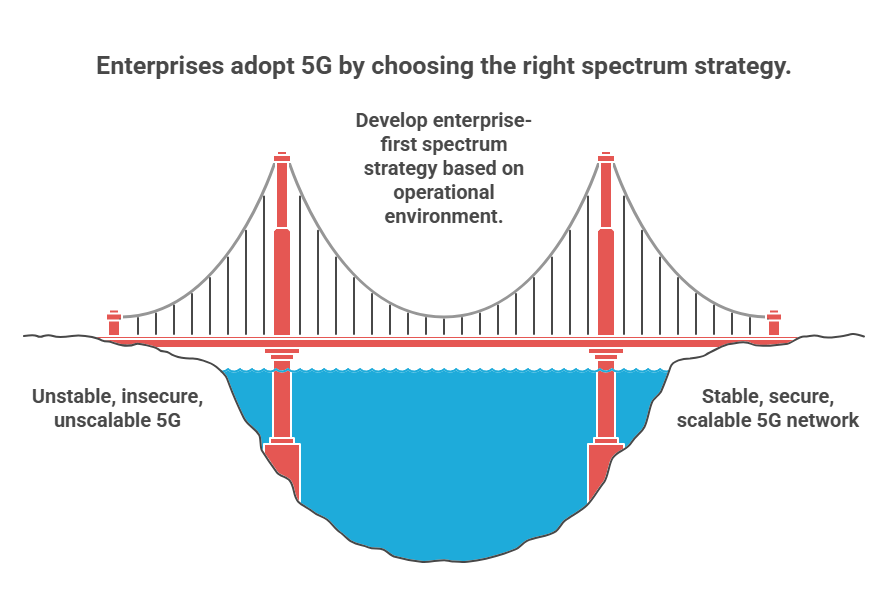
From there, they recommend a spectrum model that fits your coverage goals and compliance profile. More importantly, they ensure the radio hardware, access points, and antennas are aligned to that model from day one.
Without this clarity, even the best-designed 5G network can fail before it goes live.
#3. Inconsistent Indoor Coverage and RF Complexity
On paper, 5G promises high throughput and ultra-low latency. In practice, your coverage map will decide whether that promise reaches your actual operations. And for most enterprises, indoor coverage is where things fall apart.
5G’s higher frequency bands, especially millimeter wave, struggle with walls, metal, glass, and dense structural materials. Warehouses, production lines, high-rise offices become dead zones if the RF plan is not built from the ground up.
Many teams discover this only after deployment. Signal drops in key operational areas. Devices fail to connect. Troubleshooting becomes reactive. And productivity takes the hit.
The solution is precision RF engineering, even before the first access point is installed.
Every enterprise environment requires its own radio blueprint. This includes signal propagation models, site surveys, and hardware placement mapped against floor plans, wall materials, and expected device density.
Often, the fix involves deploying Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS), small cells, or a combination of macro and indoor radios to create seamless coverage across verticals, corners, and dense zones.
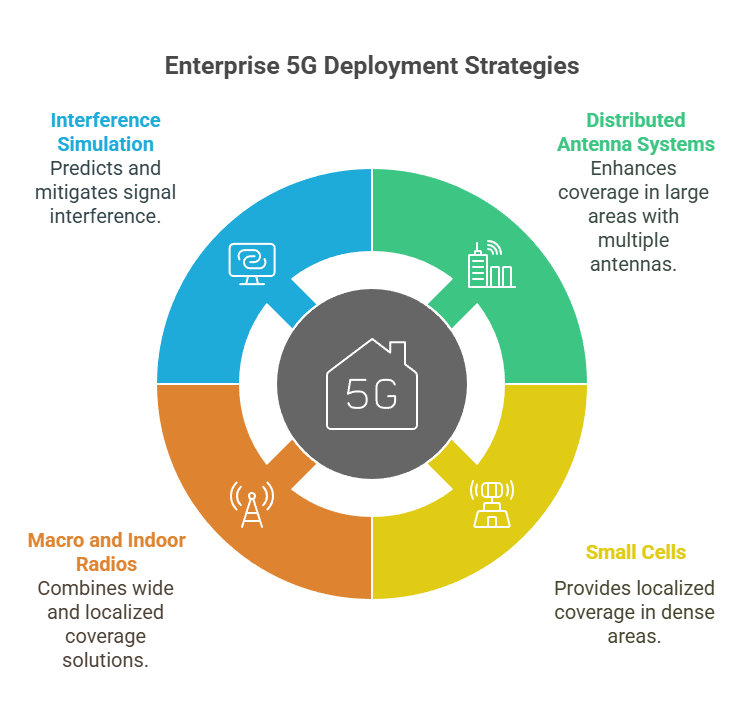
Strong integrators also simulate interference scenarios in advance, accounting for elevators, metal shelving, glass partitions, and environmental noise. This eliminates blind spots before they appear and ensures devices maintain connection quality, even at network edges.
Enterprises that skip this step end up paying for it later in both downtime and lost trust.
#4. Edge Deployment Complexity and Readiness Gaps
You cannot discuss 5G without mentioning the edge. Low latency, real-time analytics, and intelligent automation- none of it happens unless your edge architecture is ready to process data close to the source.
But here is the problem. Most enterprises are not built for edge computing. They have a central data strategy, not a distributed one. And when 5G enters the mix, they suddenly need edge nodes, localized compute, containerized applications, and new workflows their current IT team has never managed.
This creates delays. It also creates risk. Data meant to be processed instantly now bounces back to centralized systems. Latency creeps in. Performance suffers. And the benefits of 5G begin to disappear.
Solving this starts with an edge readiness framework that aligns with your real-world operations.
That includes defining where edge nodes are needed, how they connect with the 5G network, what workloads they support, and how they integrate with existing infrastructure. The focus is not just deployment, but orchestration.
The right integrators bring experience in deploying MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing), managing container platforms, and integrating these with enterprise applications, ranging from video analytics to robotics and predictive maintenance.
They also build in observability, so performance, resource usage, and security can be monitored from day one.
Enterprises that prepare their edge early do not just enable 5G, they unlock its real value.
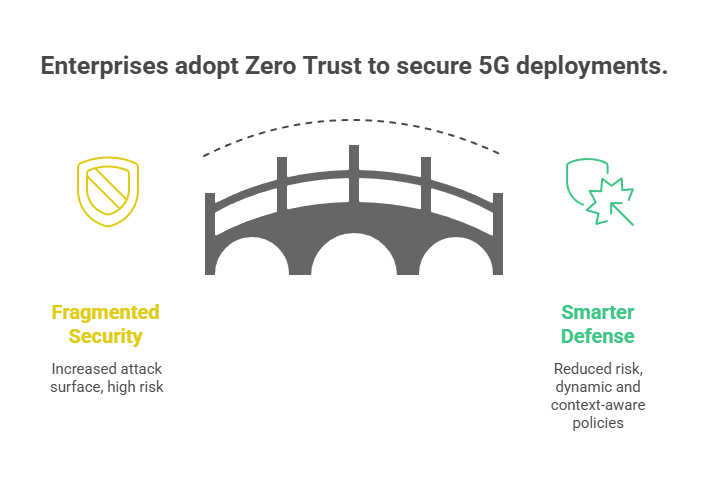
#5. Fragmented Security and Exposure Risks
Every new 5G deployment expands the attack surface. More devices. More access points. More data flowing across decentralized infrastructure. For enterprises already struggling with hybrid environments and shadow IT, this can quickly spiral into risk.
What makes 5G different is not just the volume of traffic. It is the architecture. You now have network slices. You have traffic moving between cloud, edge, and core. You have endpoints that are mobile, transient, and often invisible to traditional security tools.
Legacy security frameworks built around Wi-Fi or perimeter-based firewalls are not equipped for this. They assume static assets and predictable traffic flows. That model collapses the moment a 5G-enabled device starts talking to an edge node outside your firewall.
The fix is not more security tools. It is a new design.
Enterprises need to shift toward a Zero Trust model that treats every connection as untrusted by default. This includes continuously authenticating devices, segmenting traffic based on behavior, and enforcing policies at the edge, not just the core.
Strong integrators embed security into the 5G architecture from the start. They align with your existing IAM, SIEM, and XDR tools. They help build policies that are dynamic, context-aware, and extend across radio access, transport, and edge computing.
They also test failover scenarios and simulate attacks as part of the pre-deployment process. So security is not a layer added later, but a core design principle.
5G does not just demand faster networks. It demands smarter defense.
For enterprises aiming to future-proof their security posture while scaling 5G, integrating advanced SOC strategies is crucial. Read how SOC transformation with AI and automation can elevate your security operations.

#6. Vendor Fragmentation and Integration Failures
Most enterprise 5G projects do not fail due to hardware or software issues. They fail at the seams, where systems from different vendors are supposed to work together but don’t.
One vendor supplies the radios. Another provides the edge nodes. A third brings in orchestration. Meanwhile, the core networking stack still lives with your existing provider. None of these players are responsible for making the whole system work as one.
That responsibility falls on the enterprise. And unless you have deep in-house integration capabilities, that gap becomes the reason timelines slip, budgets stretch, and performance underdelivers.
The solution is a unified integration layer designed and managed by a partner who owns the end-to-end outcome.
This means working with a system integrator who understands how to build cohesion across vendors, protocols, and infrastructure layers. They manage compatibility from day one, align APIs and configurations, and ensure that data paths are validated before go-live.
They also act as the escalation point when vendors push blame around. Because they have already built and tested across ecosystems, they can preempt issues most teams would not see until after deployment.
With the right integrator, you are not left holding a broken stack. You are handed a working system.
#7. Skills Gaps and Operational Readiness
Even when the network is built, many 5G deployments stall in the final stretch. This is not because of technology, but because the team is not ready to run it.
5G introduces new architecture, new tools, and new workflows. Managing MEC nodes, securing dynamic network slices, and troubleshooting latency across distributed systems require skills most enterprise IT teams have never needed before.
You cannot solve this by handing over PDFs or pushing teams through a one-day training. 5G is a living, evolving system. Without hands-on understanding, issues pile up fast. Performance drops. Internal confidence erodes. And sooner or later, the system gets scaled back to something simpler and slower.
The answer is operational readiness baked into the deployment.
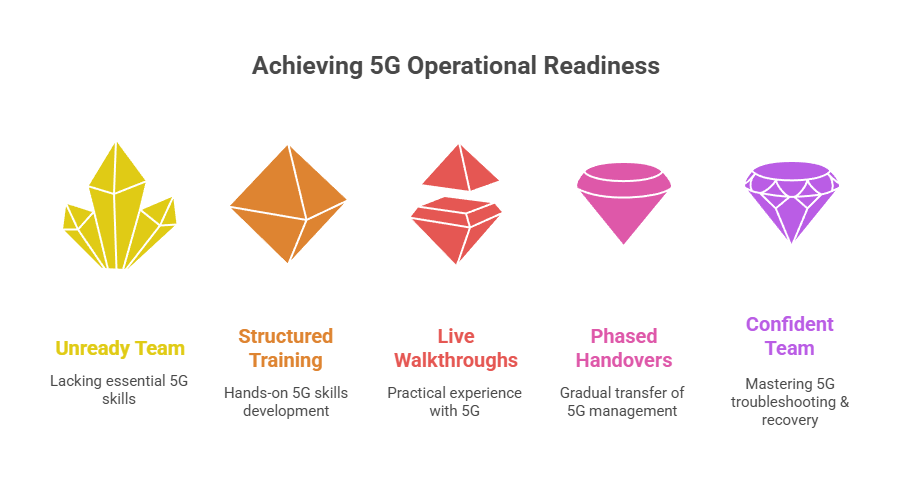
That means building a support model alongside the rollout. It includes structured training, live walkthroughs, and role-based access design that aligns with your team’s capabilities.
Strong integrators also offer co-management and phased handovers. They do not disappear after go-live. They stay involved until your internal team is fully confident handling the environment and not just from a dashboard, but from a troubleshooting and recovery perspective as well.
When the skills come up to speed with the system, performance is no longer a question. It becomes a guarantee.
The seven challenges we’ve covered are the ones that show up in every major 5G rollout, but they are not the only ones.
Many enterprises also face site access delays, last-mile fiber mismatches, cloud configuration errors, and compliance hurdles tied to data localization or industry-specific regulations. These may seem small at first, but they can slow down or derail the entire deployment if not addressed early.
That’s why the right 5G system integrator does more than just connect hardware. They plan for what goes wrong. They build with your real environment in mind. And they solve problems before they reach your operations team.
One such partner is Datacipher.
Why Datacipher is the Partner You Need for Solving 5G Deployment Challenges?
We’ve spent years solving exactly the kind of 5G deployment challenges outlined in this article and more.
As a leading system integrator and enterprise IT services provider, Datacipher has worked across sectors to re-architect legacy networks, roll out secure wireless infrastructure, and build scalable, cloud-ready environments. We know how to bring structure to the chaos.
From SD-WAN to SASE to full-stack 5G, we’ve helped clients modernize intelligently, not just for performance, but for long-term adaptability.
What sets us apart is our integration depth. We don’t just deploy radios or edge servers. We solve for the entire environment from spectrum to edge, LAN to core, policy to performance.
Because we’ve operated as a managed services provider, a network infrastructure expert, and a cybersecurity partner, we see the full picture. We know how a 5G deployment breaks. And more importantly, we know how to prevent it from breaking in the first place.
Source – Datacipher
Here’s how we help Enterprises overcome 5G Deployment Challenges
- 5G Architecture Redesign: We rework your infrastructure for seamless 5G integration from LAN to edge.
- Private LTE and DAS Implementation: We strengthen indoor coverage where 5G is weakest, using DAS and Private LTE.
- 5G Metro and Edge Solutions: We optimize deployment across urban networks and localized compute environments.
- Advanced 5G Security: We embed security at the design layer, with Zero Trust principles and real-time visibility.
- End-to-End Monitoring and Optimization: We actively monitor performance and troubleshoot issues before they impact operations.
These are not packaged offerings. They are engineered solutions tailored to your enterprise reality.
A leading manufacturing group approached us after their initial 5G deployment stalled. The radios were installed, but devices on the shop floor kept losing connectivity. Indoor coverage was inconsistent. Their internal IT team struggled with edge workloads and lacked visibility into real-time performance.
Within weeks, we re-engineered the RF plan using DAS, refreshed the switching layer, deployed MEC nodes for time-critical analytics, and trained their internal team on policy-based segmentation. The result was not just restored performance; it was a network that finally delivered on the promise of 5G.
We’ve solved these problems across industries. We can solve them for you too. Whether you’re facing one of the challenges we covered above or something that is not even on the list yet, talk to our experts. We’ll help you make 5G work the way it’s meant to.
Frequently Asked Questions
#1. How long does a typical enterprise 5G deployment take from planning to go-live?
Most enterprise 5G rollouts take between 4 to 9 months. This includes network assessment, architecture redesign, spectrum planning, deployment, and post-launch optimization. Complex sites or multi-location deployments may take longer.
#2. Do I need to replace all my existing infrastructure to make 5G work?
Not necessarily. But critical upgrades are often required. Legacy switches, outdated segmentation, and underpowered edge devices may need to be refreshed to support 5G performance and stability.
#3. What is the difference between private 5G and public 5G for enterprises?
Private 5G offers dedicated bandwidth, lower latency, and greater control over security and QoS. Public 5G shares infrastructure with other users and is managed by telecom operators, making it less customizable.
#4. Can 5G be integrated with existing SD-WAN and SASE frameworks?
Yes. In fact, successful deployments depend on it. 5G must work in harmony with SD-WAN routing policies and SASE-based security controls to deliver reliable, secure, and agile connectivity.
#5. What kind of in-house skills are needed to manage a 5G network?
Enterprises need a blend of network engineers, cloud-native ops professionals, and security architects. Skills in RF planning, containerization, and policy orchestration are increasingly important in post-deployment phases.
#6. When should I bring in a 5G system integrator, before or after deployment starts?
Before. Early involvement avoids costly rework, prevents vendor misalignment, and ensures infrastructure is ready. The most successful rollouts involve integrators from the architecture and spectrum planning phase onward.





